Hayabusa - 1st sample return from asteroid
Hayabusa is the first asteroid sample return mission to S-type asteroid 25143 Itokawa (1998SF36), which was launched by the M-V-5th launch vehicle on 9 May 2003, arrived at the asteroid on 12 Sep 2005, touchdowned for sample collection on 20 and 26 Nov 2005, and returned sample to Earth in the South Australia on 13 June 2010. Our labo contributed to the X-ray fluorescence spectrometry.
Very tiny amount of sample are obtained since it failed to shoot projectiles for sampling and acquired only the floating dust, however, many scieitific research papers by Initial Analysis teams and by International AO research groups have been published. JAXA Curation Facility was founded in 2007 for the curation of Hayabusa sample.
Hayabusa Symposium are held almost every year since 2013 for the presentation of international AO researches as well as related topics on extraterrestrial samples or planetary missions.
Kaguya - Lunar polar orbiter mission
Kaguya(SELENE) is the JAXA lunar polar orbiter mission, in collaboration with ISAS and NASDA at the beginning before unification, which was launched by the H-2A launch vehecile on 14 Sep 2007, arrived around the lunar 100km orbit on 4 Oct 2007, and finished on 11 June 2009. With 14 instruments, global mapping of the Moon in geology, mineralogy, elements, magnetic field, gravity, topigraphy, and subsurface sounding were performed. Our labo contributed to the X-ray fluorescence spectrometry. It was the top runner of lunar missions at the era, with ChangeE of China, Chandrayaan-1 of India, Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter of USA.
Hayabusa2 - 2nd sample return from asteroid
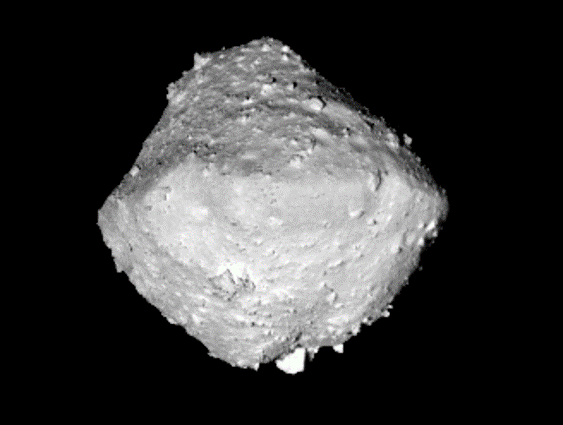
Hayabusa2 is the second asteroid sample return mission to C-type asteroid 162173 Ryugu (1999JU3), which as launched by H-2A launch vehicle on 3 Dec 2014, arrived at the asteroid on 27 June 2018, with the release of two landers of MINERVA-II and MASCOT, with the touchdowns for sample collection at two sites, with a Small Carry-on Impactor experiment, and with the target markers and MINERVA-II-2 orbiting experiments, then return sample to Earth on 5 Dec 2020.
C-type Ryugu was found of spinning top-shape, retrograde rotaion in 7h38m, the diameter of 1004 m in EQ and 847 m in NS, with the low albedo of 2%, with faint -OH band absorption in 2.7 um, with a low thermal inertia of 300 tiu. Ryugu is a rubble-pile with its average density of 1190+/-20 kg/m3 (average bulk porosity of 50%). The micro-porosity of boulders are derived as 40-50%, so that the macro-porosity is ca. 10-20%. The surface is under the gravity regine indicated by impact experiment. Our labo leads the development and science of thermal imager TIR and the small lander MASCIT.
Initial description has been conducted in JAXA Curation, with optical microscope, wighing, FTIR, and MicrOmega the NIR hyperspectral microscope. 5.4 g of sample was recovered in total, comapared with the original requirements of 0.1 g. Further detailed sample analyses will be done by Initial Analyses teams, Phase-2 Curation Teams, and then International AO research groups.
Hayabusa2/MASCOT - European collaboration
MASCOT (Mobile Asteroid Surface Scout) is the small lander released from Hayabusa2, in collaboration with DLR and CNES. The collaboration started in late 2008, and formally started in 2009. It mounted CAM(optical camera), MARA(radiometer), MAG(magnetometer), MicrOmega(NIR hyperspectral microscope). It was relased to the surface of MA-9 site on asteroid Ryugu on 3 Oct 2018, worked for 17 hours of observation.
MASCOT found the surface is covered with two types of boulders with cauliflower-like, crumbly surface and relatively flat surface. The surface is NOT covered with dusts but the surface features with fine inclusions exposed, like Tagish Lake meteorites.The surface thermal inerita is around 300 tiu, indicating highly porous materials and low strength.
Hera - 1st Planetary Defense mission & 1st misstion to binary asteroid
Hera is the ESA asteroid mission to S-type binary Didymos and Dimorphos, to be launched by Arianne-6 in 2024, and arrive in 2027. Hera is an European contribution to AIDA (Asteroid Impact and Defrection Assessment), with the NASA DART (Double-Asteroid Re-direction Teat) which is the kinetic impactor. AIDA is the first international Planetary Defense project. JAXA joins the mission by providing the thermal imager TIRI for Hera.
TIRI is a bolometer based thermal imager with an 8-point filter wheel, to investigate the thermophysical properties and the material distribution of the surface of binary asteroid system. This will be the first thermal infrared images of S-type asteroid, the comparison with spectral types and asteroid size. B-YORP effects and the detailed description of DART crater are the other objectives.
Uzume - Lunar landing and exploration of lunar holes
Uzume (Unprecedented Zipangu Underworld of the MoonExploration) is a lunar landing mission under study to explore the vertical hole with a smart lander like the SLIM, to invetigate the hole itself scientifically and to survey the feasibility for future use as the lunar base.